STABILITY
This section presents the salient highlights and equations for the stability circles drawn on the Source/Load Planes.
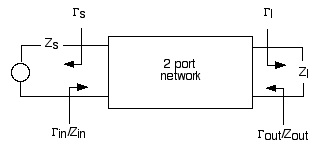
For unconditional stability:
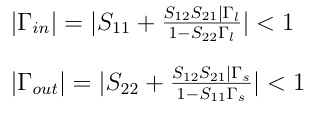
A reflection coefficient greater than unity implies a source of energy instead of a sink; or equivalently a negative resistance component. This condition results in an oscillator instead of an amplifier.
In general there are values of source or load impedances (and their respective reflection coefficients) which result in input or output reflection coefficients greater than or equal to one. In the design methodolgy, it's normal to draw the circles of stability. These circles represent the bounding case of the corresponding reflection coeffecient where it has a value of unity. The circles then define the separation of regions wherein the source/load impedances result in unstable behavior. If the above relations are solved for the bound condition of unity, the values of source/load reflection coefficients lie on circles given by:
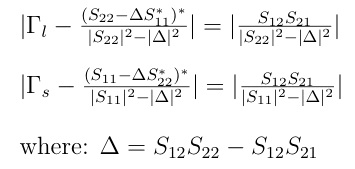
The radius and center for the Load Plane circle where the absolute magnitude of the input reflection coeffecient is equal to one and the corresponding values for the Source Plane are given by:
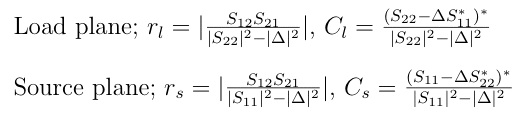
Marcus Staloff
© 2013